RAID is an advanced data storage system that is popular among individuals and enterprises as it offers enhanced storage capacity and data redundancy. RAID can be setup in different configurations depending on the requirements, such as speed, performance, data redundancy, fault tolerance, etc. In this guide of Cubvh, we will explain the RAID in detail and some popular types of RAID configurations. We will also discuss a secure way to perform RAID data recovery and tips to prevent data loss in the event of RAID array failure.
Table of Contents
What is RAID?
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent or Inexpensive disks is a complex setup of multiple physical drives combined together to form a single logical storage unit. The member drives can be setup in different configurations, such as RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, etc., according to speed, data security, and data redundancy.
RAID 0, 5, and 6 use Striping in which data is split into smaller blocks and each block is stored on separate member drives. RAID 1 uses Mirroring that creates exact replicas or copies of the data present on the primary drive onto the secondary member drives.
Along with this, some RAID configurations or levels, such as RAID 5, RAID 6, and nested RAID arrays (RAID 10, and above), use Parity or fault tolerance. Parity is calculated using various codes like XOR, Reed-Solomon code, EVENODD etc., and is stored on a separate block present on the RAID. Parity of a RAID array dictates the number of drive failure it can sustain before complete array failure. For example, RAID 5 has a fault tolerance of 1 drive failure while RAID 6 has a fault tolerance of 2 drives failure.
Here is a table showing details of popular RAID configurations.
| RAID Configuration | Data Storage Technology | Min. No. of Drives Required | Fault Tolerance | Possibility of Recovering Data |
| 0 | Striping | 2 | NA | No |
| 1 | Mirroring | 2 | 1 drive failure | Yes |
| 5 | Striping + distributed parity | 3 | 1 drive failure | Yes |
| 6 | Striping + Double distributed parity | 4 | 2 drive failure | Yes |
What causes Data Loss in RAID Systems?
For effective data and file restoration from RAID, it is essential to understand the causes and issues that can result in data loss from a RAID array. Here are some common reasons for data loss in RAID systems:
- Hardware Issues – Hardware, like RAID controller, SATA cables and connectors, storage drives, drive enclosure, etc., could malfunction or fail, preventing you from accessing the data.
- Software Issues – RAID arrays use RAID management software or the operation system to function. Errors or bugs in these software could result in inaccessible RAID array.
- Human Errors – Sometimes, misconfiguration of RAID array during setup or rebuild, improperly powering down the array, etc., can cause integrity issues and result in partial or complete data loss.
- Physical Damage – Power surges or cuts, unsuitable environmental conditions, etc., can cause damage to the storage drives. Overheating or accumulation of dust can also impact the RAID array.
How to Recover Data from a Failed RAID Array?
You can recover data from a failed RAID array if the number of drive failure is within the permissible limit, i.e., fault tolerance of the RAID configuration. If this number exceeds, there will be a complete RAID array failure, resulting in permanent data loss.
Here is a general systematic approach that should be implemented to perform RAID data recovery.
Step 1: Diagnose the issue and the member drives. Diagnostics will help to identify the type of issue and the extent of failure.
Step 2: Disk Cloning is crucial as it involves creating a clone of the disk drives that act as a backup in case RAID array fails during recovery.
Step 3: Recovery is the final step that involves either rebuilding the RAID array or using a specialized RAID data recovery software to safely recover the data from the failed RAID array.
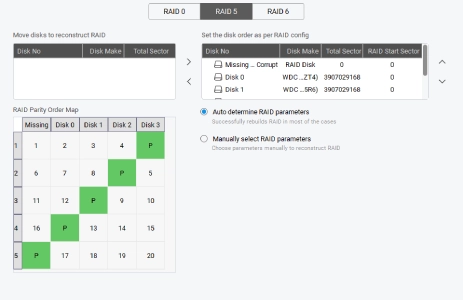
Rebuilding the failed RAID array involves replacing the faulty SATA connectors, RAID controller, or hot-swapping the degraded member drive/s. However, it is a risky process as rebuild time increases with large capacity drives. Moreover, any interruption, like power cut, RAID crash, URE, etc., during the rebuild process may cause permanent data loss.
Hence, you can use a specialized RAID data recovery software, like Stellar Data Recovery Technician. The software is designed to safely recover data from a failed or an inaccessible 0, 5 or 6 RAID array. The software virtually rebuilds the failed RAID array and performs RAID data recovery on the virtually reconstructed array. The software is capable of recovering data in the following scenarios:
- Critical data recovery
- Uncertain RAID configuration parameters
- Complex RAID failure (RAID 6, RAID 1+0, etc.)
You can also use this software to recover lost or deleted data and files from HDDs, SSDs, SD cards, flash drives, optical media (CD/DVD), and other storage media. Furthermore, you can use it to monitor the health of the drives or create a bootable media for retrieving data from crashed or unbootable Windows PC.
Tips to Prevent Data Loss due to RAID Failure
- Do not consider RAID as a backup.
- Use the 3-2-1 backup technique to take backup of important files.
- Cease all operations on the RAID array in case of a drive failure.
- Keep a specialized RAID data recovery software.
Conclusion
Recovering data from a failed RAID array requires proper understanding of the architecture and the underlying issue. However, using a powerful RAID data recovery software can help simplify the process and improve the chances of recovering data. Implementing effective strategies to recover data from RAID arrays can help protect data and prevent unprecedented downtimes.
